Are you looking to improve your chromatography analysis? Understanding reversed-phase column selectivity is key to achieving accurate and reliable results. By utilizing a reversed-phase column selectivity chart, you can optimize your chromatographic separations.
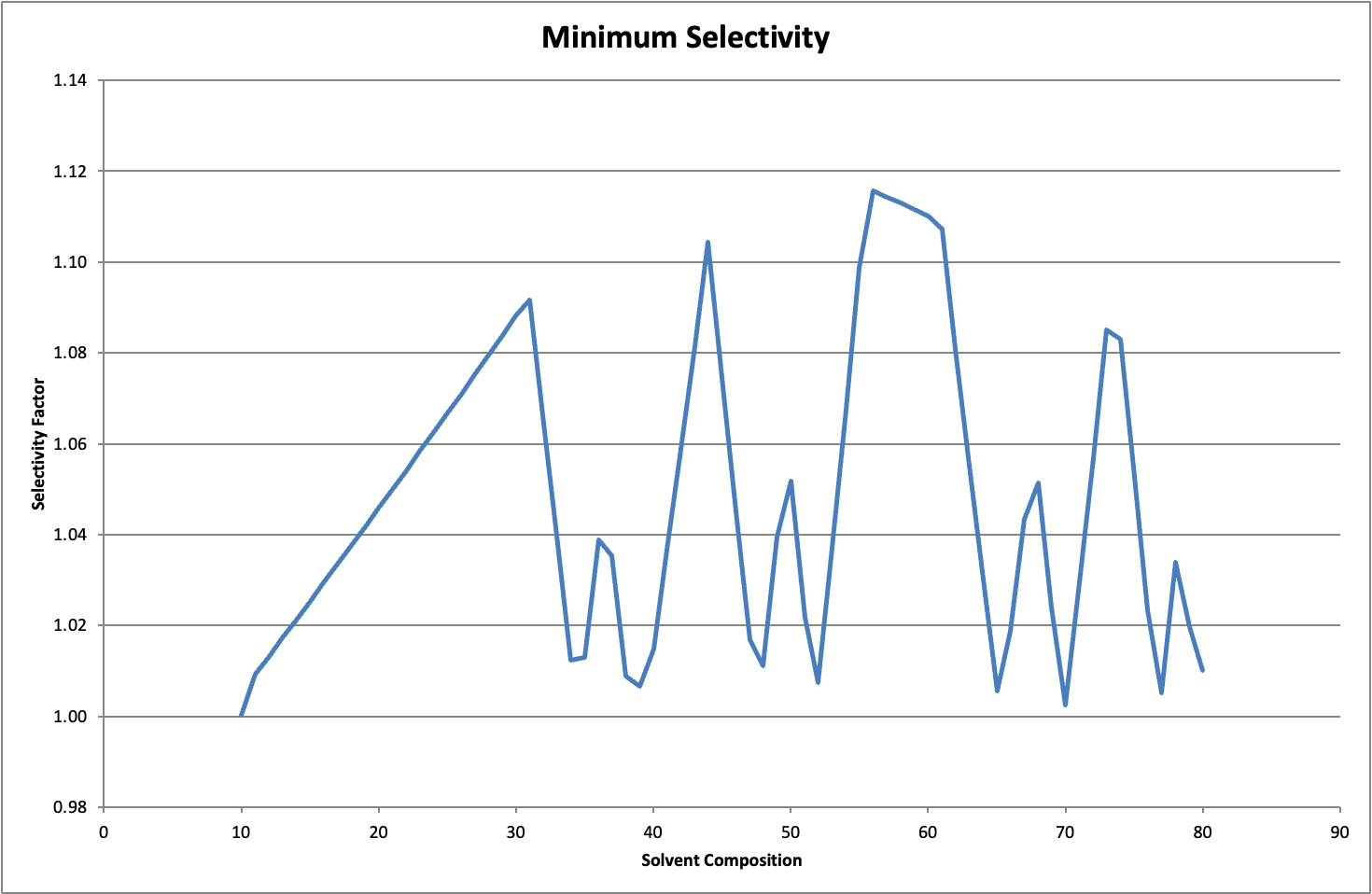
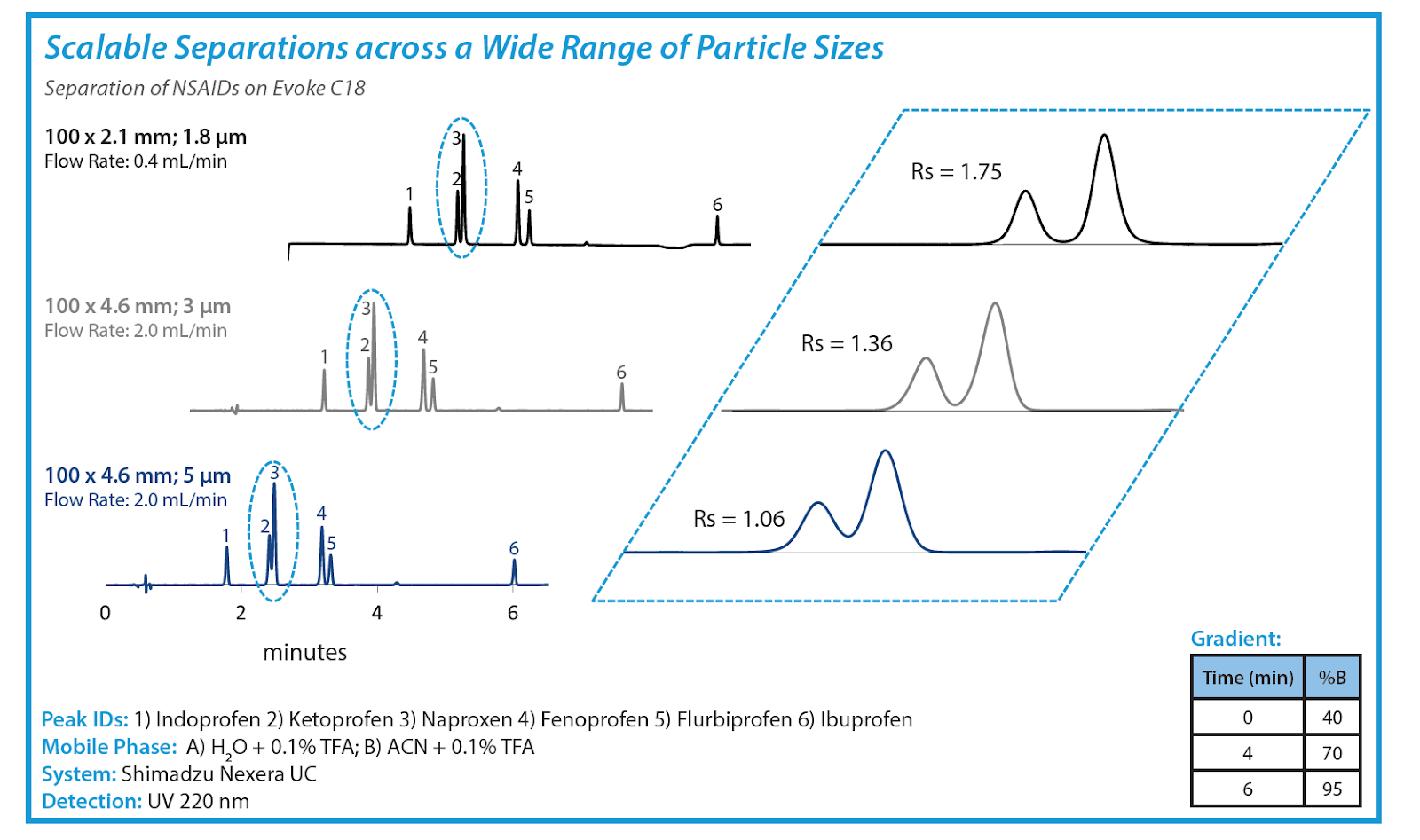
Reversed-phase chromatography is a widely used technique in analytical chemistry for separating compounds based on their hydrophobicity. The selectivity of the column plays a crucial role in determining the separation efficiency and resolution of the analytes.
Reversed Phase Column Selectivity Chart
Reversed Phase Column Selectivity Chart
When selecting a reversed-phase column for your chromatographic analysis, it’s essential to consider the selectivity of the stationary phase. A reversed-phase column selectivity chart provides valuable information on the types of analytes that can be separated effectively using a specific column.
By referring to a reversed-phase column selectivity chart, you can choose the most suitable column for your application based on factors such as analyte polarity, molecular weight, and functional groups. This allows you to achieve optimal separation and detection of analytes in your samples.
Furthermore, a reversed-phase column selectivity chart can help you troubleshoot issues related to peak shape, resolution, and sensitivity in your chromatographic analysis. By understanding the selectivity of the column, you can make informed decisions to improve the overall performance of your chromatography system.
In conclusion, utilizing a reversed-phase column selectivity chart is essential for optimizing chromatographic separations and achieving accurate results in your analytical work. By selecting the right column based on selectivity considerations, you can enhance the efficiency and reliability of your chromatography analysis.